|
| Glaucoma Vision |
Eye specialists routinely check visual keenness, or sharpness of vision dependent on how well the patient can peruse an eye graph.
Glaucoma is a genuine eye condition in which the optic nerve ends up harmed, more often than not because of expanded weight in the eye.
In spite of the fact that glaucoma as a rule doesn't cause clear side effects at first, some early cautioning signs may demonstrate its beginning.
With incite treatment for glaucoma, you might have the capacity to forestall or moderate the loss of your fringe or side vision. Fringe vision misfortune (otherwise called a fringe field imperfection) can weaken into limited focus. At the point when the main usable vision is from the focal point of the eye, it can make the impact of seeing through a tube or passage.
In the event that glaucoma proceeds without treatment, your vision — notwithstanding when looking straight ahead — can decline until the point when you turn out to be thoroughly visually impaired. Glaucoma is one of the main sources of visual deficiency, alongside age-related macular degeneration and waterfalls. (3)
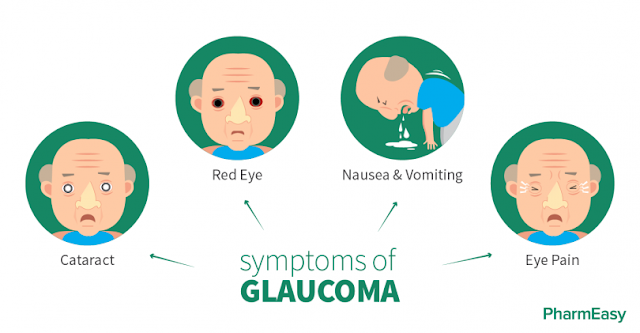
Indications of Glaucoma
Visit an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) quickly for an entire eye exam on the off chance that you see any of these notice signs:
- Trouble modifying your vision to an obscured room
- Inconvenience concentrating on close or far items
- Abnormal affectability to light or glare
- Squinting or flickering at a brilliant light or a glare
- Change in the shade of your iris (hued part of the eye)
- Red-rimmed, encrusted, or swollen eyelids
- Tenacious agony in or around your eyes
- Twofold vision
- Dim spot at the focal point of your vision
- Seeing lines and edges that appear to be wavy or twisted
- Overabundance tearing or watery eyes
- Dry eyes that tingle or consume
- Seeing spots or phantom like pictures
- Look for crisis therapeutic consideration on the off chance that you encounter any of the accompanying side effects:
- Serious cerebral pain and eye torment
- Sudden loss of vision in one eye
- Sudden dim or obscured vision
- Flashes of light or dark spots in your vision
- Radiances or rainbows around light in your vision
Indications may travel every which way at first, or compound after some time.
Glaucoma Analyze
Customary eye exams by an eye specialist are the most ideal approach to identify glaucoma.
The American Foundation of Ophthalmology (AAO) prescribes that everybody get a standard eye exam by age 40, or sooner in the event that you have chance elements for eye infection, for example, hypertension or diabetes. (5)
Amid an eye exam, the specialist will gather a patient's medicinal history and check a few variables, including visual keenness (sharpness of vision dependent on how well the patient can peruse an eye outline). Following on a thorough eye exam, the specialist can exhort you on how frequently to have your eyes checked.
The AAO prescribes glaucoma screening:
Like clockwork starting at age 40, on the off chance that you don't have any hazard factors
At regular intervals in case you're over age 65 or at high hazard (6)
Glaucoma Test
Amid your visit, the eye specialist may play out various distinctive systems, including:
Glaucoma Examination
Your specialist will utilize unique eye drops to enlarge your understudies, which enables all the more light to enter the eye and makes it simpler for the specialist to look at the back of your eye.
In patients with glaucoma, a thorough expanded exam may demonstrate changes in the shape and shade of the optic nerve strands.
Notwithstanding recognizing glaucoma, expansion makes it simpler for your specialist to analyze different ailments — including retinopathy because of diabetes or hypertension, a confined retina, or macular degeneration — at their soonest arranges.
The National Eye Organization (NEI) prescribes that individuals age 60 and more seasoned get a yearly enlarged eye exam.
Know that widening can obscure your vision and make your eyes more delicate to light. This can influence your capacity to peruse, drive, or labor for a couple of hours.
Different tests used to distinguish glaucoma include:
Glaucoma Tonometry Test
This test estimates the weight inside your eye. It's easy and causes insignificant distress.
The most exact types of the test measure the power expected to quickly straighten a zone of your cornea (clear layer at the front of the eye).
To begin with, your specialist will utilize eye drops to numb the surface of your eye and apply an orange color to incidentally recolor the eye.
At that point your specialist will put an instrument known as an opening light before you. Resting your button and brow on a help keeps your head unfaltering as the opening light is advanced until the tip of the gadget just contacts your cornea.
A blue light on the light makes the orange color sparkle green. Your specialist will look however an eyepiece on the light, and alter a dial on the gadget to peruse your eye weight.
Specialists can rather utilize a hand-held, pencil-formed gadget that contacts your eye and quickly records the weight.
Another approach to quantify eye weight is with a gadget that shoots a puff of air into your eye. As you gaze into the machine, the specialist sparkles a light into your eye, and afterward you'll feel a speedy puff of air.
This technique causes no uneasiness. The machine estimates your eye weight dependent on how the light reflections change as the air hits your eye.
Gonioscopy
In this technique, your specialist looks at the waste point of your eye utilizing a unique contact focal point. The point is the place the cornea and the iris meet.
Ophthalmoscopy
This technique gives your specialist a chance to analyze the back of your eye (known as the fundus), including the retina, optic plate, and veins.
Pachymetry
A test called a pachymeter is utilized to quantify the thickness of the cornea. Corneal thickness is critical in light of the fact that it can influence the perusing of intraocular eye weight (IOP). High eye weight is a hazard factor for glaucoma. Individuals with thin corneas may have incorrectly low IOP readings, while individuals with thick corneas may demonstrate a higher-than-genuine IOP. (11)
Perimetry
Otherwise called a visual field test, this method estimates the extent of focal and fringe vision and distinguishes vulnerable sides.